Customer Development & User Research Workshop
From Customer Discovery to Product-Market Fit: A Constructor University Special Edition
✨ Welcome & Workshop Overview
Welcome to our Customer Development and User Research workshop! Today, we'll explore how to validate ideas effectively using customer development, design thinking, and user research methodologies.
🎯 Workshop Objectives
By the end of this session, you will be able to:
- Apply core principles of customer development, design thinking, and user research
- Understand why problem-solution fit is essential for any business
- Identify and avoid common validation pitfalls
- Leverage AI tools to enhance research and analysis (with proper understanding of limitations)
- Develop a foundational validation plan for your own projects
🗺️ Workshop Structure
- Module 1: The Foundation - Why Customer Development is Essential
- Module 2: Customer Development, Design Thinking & User Research Principles
- Module 3: Qualitative Research Techniques & Best Practices
- Module 4: Modern Tools & AI in Research (Benefits & Limitations)
- Module 5: Handling Negative Feedback & Building Resilience
- Module 6: Putting It All Together - Crafting Your Strategy
🔍 Module 1: The Foundation - Why Customer Development is Essential
⚠️ Critical Truth: Problem-Solution Fit is a Must
If you are not doing customer development, you are not building a real business - regardless of whether you're a startup or an established company.
Here's the reality check:
- 🚀 For Startups: Without customer development, you're just building features in a vacuum - not a viable business
- 🏢 For Established Companies: Without ongoing customer understanding, you're slowly losing your competitive moat to those who do listen to customers
- 💡 The Universal Truth: Customer needs evolve constantly - companies that stop listening become irrelevant
Customer development is essential for everyone because:
- 💰 Resource Efficiency: Understanding customers before building saves time, money, and prevents failure
- 🎯 Market Relevance: Customer insights drive innovation and competitive advantage
- 📈 Sustainable Growth: Companies that understand their customers grow faster and last longer
- 🛡️ Risk Mitigation: Customer validation reduces the risk of building something nobody wants
💡 Bottom Line: Whether you're a day-one startup or a Fortune 500 company, customer development isn't optional - it's the foundation of sustainable business success.
📊 The Data Speaks: Why Customer Development Matters
In today's rapidly evolving market, customer understanding is no longer optional—it's essential for survival. The statistics paint a sobering picture of what happens when businesses ignore their customers:
- ~90% of startups fail
- ~10% collapse in their first year
- Small businesses: 20% fail in year one, 70% fail by year ten
💡 Key Insight
The #1 reason for startup failure: "No Market Need" (42%)
This signals systemic weaknesses in early-stage validation and understanding user needs.
🚫 Common Validation Pitfalls
- Founder's bias: Overlooking actual customer problems
- Skipping/misinterpreting market research: Making assumptions without data
- The "build-first trap": Developing solutions before validating problems
- Poor planning: 78% of failed businesses had no/poor business plan
🚗 Case Study: Volkswagen Digital:Lab - Customer Development in Action
Volkswagen faced a critical challenge: their traditional waterfall development was "falling out of fashion due to limited ability to adjust course as new information was uncovered." Their solution? Create a radical experiment in customer development:
🔄 Deliberate Methodology Transformation
- 🏙️ Separate Berlin location - away from traditional VW culture
- 🤝 Partnered with Pivotal Labs - "to leverage Pivotal's agile experience and acquire a new competency for VW"
- 📊 Daily agile standups - discussing progress on various Lab products
- ⚡ Short development sprints - allowing quick reaction to user lessons
🎯 Problem-First Mindset (Design Thinking in Practice)
"The traditional model is for business managers just to request IT teams to build something. But we want to help solve the problems of the actual users. One of the most repeated questions at Digital:Lab is, 'Okay, but what is the problem?'"
🔬 Rigorous User Research & Validation
- 📋 6-week Discovery & Framing phase - standard for every project
- 📊 Quantitative user research - found 50% drop-off rate in existing identity solution
- 🎯 MVP thinking - building smallest viable solution to validate assumptions
- 👥 User-centric solutions - IdentityKit became "user- and developer-friendly"
💬 Powerful Quote from Jochen Scherl, Digital:Lab Lead
"I'm very proud that we stopped six projects in the first year because we found out there was no need. There was an idea but there was no need. Normally stakeholders have an idea and they spend money and you find out after one-and-a-half years that there's no need. At the Digital:Lab, we would find out in six weeks."
💡 Key Lesson: Customer development isn't just about validating good ideas - it's about quickly invalidating bad ones before wasting resources.
💬 Discussion Questions
Think about and share in chat:
- Cultural Challenge: VW's most repeated question became "What is the problem?" instead of "Build this feature." What would it take to shift your organization to this problem-first mindset?
- Success Metrics: Jochen Scherl was "proud to stop six projects" because there was no real need. How would you convince stakeholders that stopping projects early is actually success?
- Speed vs. Thoroughness: 6 weeks vs. 1.5 years to discover "no need" - what would be the biggest barrier to achieving this speed in your context?
💭 Module 2: Customer Development, Design Thinking & User Research Principles
🤔 What are Customer Development, Design Thinking & User Research?
These methodologies are similar in essence but have different focuses:
👥 Customer Development
- 🎯 Focus: Discovering and validating customer needs
- 📊 Approach: Systematic hypothesis testing
- 🔄 Process: Customer Discovery → Customer Validation → Customer Creation → Company Building
- 💼 Origin: Steve Blank's lean startup methodology
🧠 Design Thinking
- 🎯 Focus: Human-centered problem solving
- 📊 Approach: Empathy-driven innovation
- 🔄 Process: Empathize → Define → Ideate → Prototype → Test
- 💼 Origin: IDEO and design consultancies
🔗 The Connection
All three approaches share the same core principle: understand your users deeply before building solutions. They can be called differently but in essence, they solve the same fundamental problem - reducing the risk of building something nobody wants.
🚗 Real-World Integration: VW Digital:Lab's Methodology Stack
VW Digital:Lab successfully combined all three approaches in practice:
- 🔄 Agile Development: "Short development sprints allowed software developers to react quickly to new events and lessons from users"
- 🧠 Design Thinking: "One of the most repeated questions at Digital:Lab is, 'Okay, but what is the problem?'" - problem-first mindset
- 👥 User Research: "Researching customer behavior, the Lab team found the existing identity solution struggled... 50% drop-off rate"
💡 Key Insight: They didn't choose one methodology - they integrated all three to create a comprehensive validation system.
🎨 Miro Board Exercise
Activity: Customer Development Canvas
Work in teams to fill out a customer development canvas on our shared Miro board:
- 🎯 Customer Segments: Who are your potential customers?
- 🔍 Problems: What problems do they face?
- 💡 Solutions: What solutions might address these problems?
- 📊 Hypotheses: What assumptions are you making?
- 🧪 Tests: How will you validate these hypotheses?
Access the Miro board: [Link will be provided during workshop]
🔬 Module 3: Qualitative Research Techniques & Best Practices
📊 Understanding Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
💡 Key Insight: The Role of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research mainly serves for insights gathering - it is your hypothesis validation and improvement because it is faster to talk with a few customers than to develop something and market it.
But the real verification happens when you earn money with your product.
As a startup founder, you need to talk with people and be able to listen to what they are saying. It can be disillusioning and might hurt, but it is an important part of the process.
🗣️ Qualitative Methods
- 👥 User Interviews: In-depth conversations to understand needs, motivations, and pain points
- 👁️ Contextual Inquiry: Observing users in their natural environment
- 👪 Focus Groups: Facilitated discussions with multiple users
- 🧪 Usability Testing: Observing users interact with prototypes
- 📔 Diary Studies: Users document experiences over time
📈 Quantitative Methods
- 📝 Surveys: Collecting structured data from many users
- 📊 Analytics: Analyzing user behavior data
- 🔄 A/B Testing: Comparing performance of different versions
- 🃏 Card Sorting: Understanding how users categorize information
- 📏 Benchmark Testing: Measuring against standards or competitors
🎙️ Effective User Interviews
- 📋 Prepare thoughtfully: Create an interview guide with open-ended questions
- 🔍 Start broad, then narrow: Begin with context, then dive deeper
- ❓ Use the "Five Whys" technique: Probe to uncover root causes
- 👂 Listen more than you speak: Let users tell their stories
- 👀 Watch for behavioral signals: Note body language and emotional responses
- ⚠️ Avoid leading questions: "Tell me about your experience" vs. "Was your experience good?"
- 💬 Capture verbatims: Record exact phrases users say about their problems
💬 Chat Exercise: Open-Ended Questions
Think about and add your most important open-ended question about your own product in the chat right now. Let's see how it looks like.
Examples of good open-ended questions:
- "Tell me about the last time you faced [problem your product solves]"
- "Walk me through your typical day when dealing with [relevant situation]"
- "What's the most frustrating part about [current solution/process]?"
🤖 Module 4: Modern Tools & AI in Research (Benefits & Limitations)
🧠 AI's Role in User Research & Validation
AI is transforming how we conduct research, analyze data, and validate ideas. Key benefits include:
- 🛡️ Risk reduction through deeper insights
- 💰 Enhanced investor credibility with data-backed decisions
- 📊 Optimal resource allocation
- ⚡ Dramatically accelerated insight generation
Potential impact: Reduce validation costs by up to 83%, condense timelines from months to 72 hours
⚠️ The Problem with AI Tools for Beginners
When you start doing and analyzing user interviews via LLMs without experience, you face the main problem:
- 🔧 Same as with coding: If you didn't build software before, you'll be able to build a prototype but nothing more
- 📊 No evaluation framework: You don't have "evals" - ways to judge if the AI output is good enough
- 📝 Text-heavy output: It's not visual, it's hard to understand compared to well-structured analysis
- 🎯 Lack of context: AI doesn't understand your business context and customer nuances like you do
- 🧠 Missing experience: You need to understand what good insights look like before AI can help you find them
Using ChatGPT and similar tools is great, but you need foundational knowledge first.
🔄 AI for Qualitative Research Synthesis
- ⚠️ Traditional Challenges: Time-consuming, biased, hard to scale
- ✨ AI Capabilities:
- 🎙️ Automated Transcription (saving hours)
- 🧠 Semantic AI Synthesis (understanding meaning, context, nuances)
- 😊 Sentiment, Intent, Emotion Analysis
- 🏷️ Automated Coding, Tagging, Categorization
- 🔍 Identification of Pain Points, Needs, Behaviors
- 🛠️ Example Tools: AxWise, Insight7, Quals.ai, NVivo (with AI), Dovetail
💡 AxWise Approach to Research Synthesis
AxWise transforms how teams analyze qualitative data by providing visual, structured insights that are easier to understand and act upon compared to raw text outputs from general AI tools.
💪 Module 5: Handling Negative Feedback & Building Resilience
🎯 Critical Mindset Shift
Your task is not about ego, but to build business and earn money.
Negative feedback is not actually "negative" - it's just words from a person's perspective that can help you build a better product.
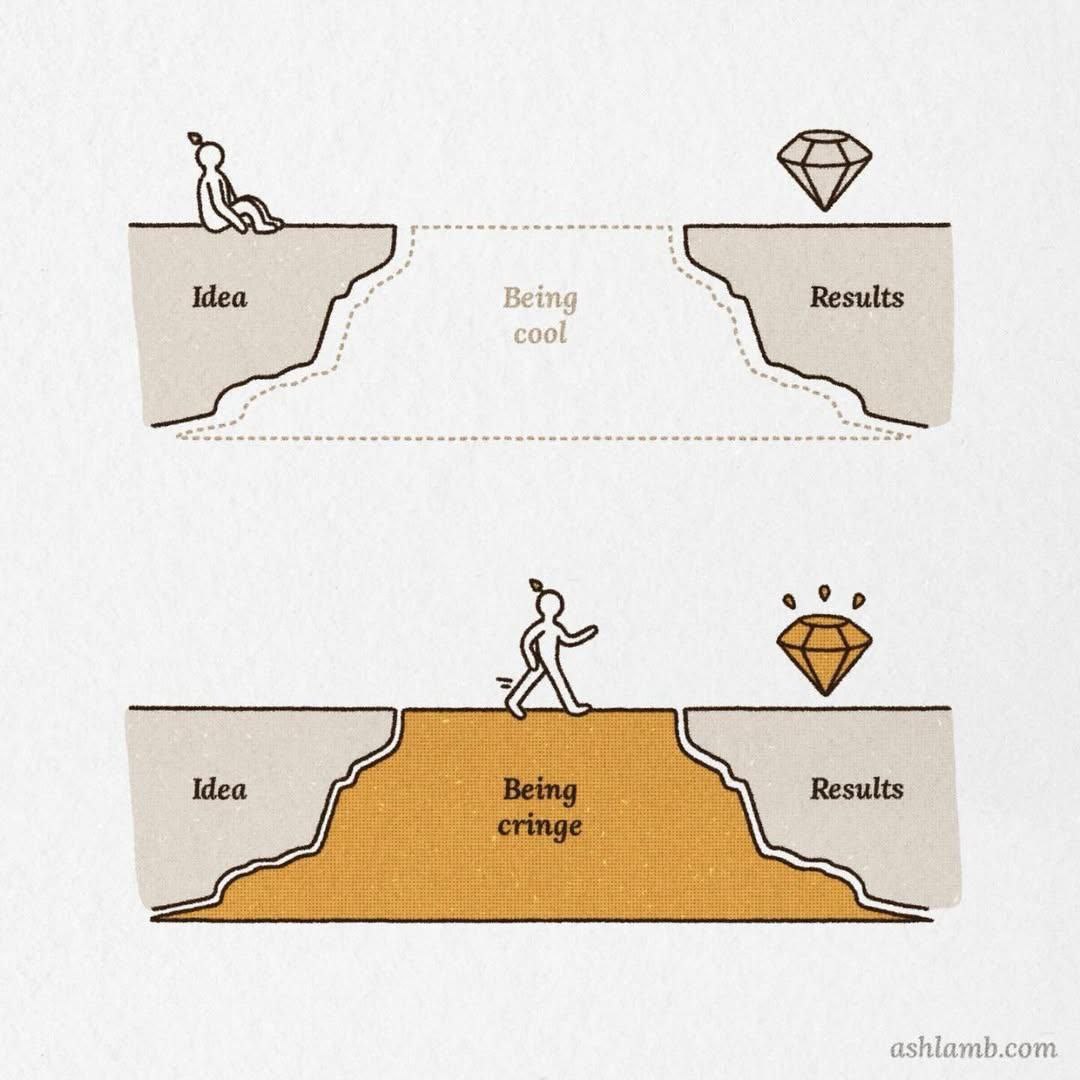
Sometimes you need to embrace being "cringe" to build something people actually want
🔄 Reframing "Negative" Feedback
❌ Ego-Driven Thinking
- "They don't understand my vision"
- "This feedback is wrong"
- "They're not my target customer"
- "I know better than they do"
- "This hurts my feelings"
✅ Business-Driven Thinking
- "What can I learn from this perspective?"
- "How does this help me build a better product?"
- "What underlying need is being expressed?"
- "How can I validate or invalidate this concern?"
- "What would make this person pay for my solution?"
🛡️ Building Feedback Resilience
- 📊 Separate emotion from data: Treat feedback as information, not personal attacks
- 🔍 Look for patterns: One person's opinion vs. multiple people saying the same thing
- ❓ Ask follow-up questions: "Can you tell me more about that?" "What would ideal look like?"
- 🎯 Focus on the problem, not the solution: Users are great at identifying problems, less reliable at proposing solutions
- 💰 Remember the goal: You're building a business, not seeking validation
🧠 Mindset Exercise
Think of the harshest feedback you've received about your idea. Now rewrite it from a business perspective:
- What specific problem or concern does this feedback highlight?
- How could addressing this concern make your product more valuable?
- What questions could you ask to better understand this perspective?
- How might this feedback help you reach product-market fit faster?
🎭 The "Cringe" Factor
Sometimes building a successful product means:
- 🗣️ Asking questions that feel obvious or "dumb"
- 🔄 Pivoting when your original idea doesn't work
- 📞 Making cold calls to potential customers
- 🎤 Presenting ideas that aren't fully polished
- 💬 Having uncomfortable conversations about money and value
Remember: Being "cringe" for a few months is better than building something nobody wants for years.
🚀 Module 6: Putting It All Together - Crafting Your Strategy
📋 Your Customer Development Action Plan
🎯 Step 1: Define Your Hypotheses
Write down your key assumptions:
- Customer Segment: Who do you think your customers are?
- Problem: What problem do you think they have?
- Solution: How do you think your product solves it?
- Value Proposition: Why would they choose you over alternatives?
🔍 Step 2: Design Your Research
Plan your validation approach:
- Interview Questions: 5-7 open-ended questions to test your hypotheses
- Target Participants: 10-15 people from your assumed customer segment
- Success Criteria: What would prove/disprove your assumptions?
- Timeline: When will you complete these interviews?
📊 Step 3: Analyze & Iterate
Process your findings:
- Pattern Recognition: What themes emerged across interviews?
- Hypothesis Testing: Which assumptions were validated/invalidated?
- Pivot Decisions: What changes do you need to make?
- Next Steps: What's your next round of validation?
🛠️ Tools & Resources
📝 Research Tools
- Calendly: Easy interview scheduling
- Zoom/Google Meet: Remote interviews
- Otter.ai: Automated transcription
- Miro: Visual analysis and mapping
- Typeform: Follow-up surveys
🤖 AI-Powered Analysis
- AxWise: Comprehensive interview analysis
- Insight7: Automated theme extraction
- Dovetail: Research repository
- ChatGPT: Quick analysis (with limitations)
- Claude: Structured data processing
💡 Pro Tip: Start Small, Think Big
Begin with 5-10 interviews to test your biggest assumptions. Don't try to validate everything at once. Focus on the riskiest hypotheses first - usually around problem-solution fit.
🚗 VW Digital:Lab Validation Framework
Remember Jochen Scherl's approach: "We would find out in six weeks" instead of spending 1.5 years. Apply this systematic methodology:
📋 The 6-Week Discovery & Framing Process
- 🔍 Problem validation first - "What is the problem?" before any solution
- 👥 User research with data - quantify pain points (like the 50% drop-off rate)
- 🎯 MVP definition - smallest thing to validate core assumptions
- 📊 Success metrics defined - know what "validated" looks like
🚫 Validation as Success Metric
- 🏆 Celebrate stopping projects - "proud that we stopped six projects"
- 💰 Measure resources saved - not just projects launched
- ⚡ Speed of invalidation - weeks vs. years of discovery
- 🔄 Iterative learning - short sprints with user feedback
🎯 Problem-First Culture
"We want to help solve the problems of the actual users" - shift from feature requests to user problem solving
🎯 Success Metrics
How to know if your customer development is working:
- 📈 Increasing Clarity: Your understanding of the problem becomes more specific
- 🎯 Consistent Patterns: Multiple customers describe similar pain points
- 💰 Willingness to Pay: Customers express interest in paying for a solution
- 🔄 Referral Behavior: Customers suggest others who have the same problem
- ⚡ Urgency Signals: Customers are actively seeking solutions now
🎉 Workshop Conclusion & Next Steps
🔑 Key Takeaways
- 🎯 Customer development is essential - not optional for any business
- 🗣️ Qualitative research provides insights - but revenue provides validation
- 🤖 AI tools are powerful - but require foundational knowledge to use effectively
- 💪 Negative feedback is valuable data - not personal attacks
- 🚀 Start small and iterate - don't try to validate everything at once
📅 Your 30-Day Challenge
Week 1: Hypothesis Formation
- Define your customer segment and problem hypotheses
- Create interview guide with 5-7 open-ended questions
- Identify 15-20 potential interview participants
Week 2-3: Research Execution
- Conduct 10-15 customer interviews
- Take detailed notes and record (with permission)
- Look for patterns and unexpected insights
Week 4: Analysis & Planning
- Analyze findings and test hypotheses
- Decide on pivots or iterations needed
- Plan next round of validation
📚 Additional Resources
- 📖 Books: "The Mom Test" by Rob Fitzpatrick, "The Lean Startup" by Eric Ries
- 🎓 Courses: Steve Blank's Customer Development course, IDEO Design Thinking
- 🛠️ Tools: AxWise for AI-powered analysis, Miro for visual mapping
- 🌐 Communities: Indie Hackers, Product Hunt, local startup meetups
👨💼 About the Presenter
Vitalijs Visnevskis - Founder of AxWise.de
Expert in AI-powered User Research & Customer Development